I recently came across a scenario in kafka where our brokers have been pushed out of the ISR and partitions have been declared under replicated. This situation has been going on for weeks & our brokers cant seem to catch up. Due to this paralysis, partition reassignment is also failing/stuck.
Inspired by this blog post on kafka storage internals, i came up with a procedure to bring the brokers back into ISR.
Before i go into the procedure, here are few things to understand:
- Offset of message in a partition remains the same both in the leader broker and replica broker.
- Position of message having a certain offset in the log file in leader broker may or may not be the same in replica broker. It does not matter if the position matches or not because a consumer is only interested in offset not where its located in the file. But in practice, based on my tests, i have noticed its the same and i believe it should be the same. if a message with offset 0 in leader broker, is say 10 bytes in length, offset 1 should be at position 11, so i would think the same applies to replica broker as messages are ordered and storing the message at a different position in replica broker does not make sense, it complex to have such logic.
- There are 3 important files in a broker log.dir to take note of :
- replication-offset-checkpoint -> for a topic partition, the broker stores the latest offset it has successfully replicated.
- recovery-point-offset-checkpoint -> for a topic partition, broker stores/tracks which messages (from-to offset) were successfully check pointed to disk.recovery-point-offset-checkpoint.
- log-start-offset-checkpoint -> for a topic partition, broker stores the first/earliest offset it has available at the moment. refer here.
- The format of the above 3 files is the following:
- first line is version
- 2nd line = number of info lines
- each line has topic name followed by partition followed by offset

Test Conditions to induce Under replication:
- 3 brokers, 1 zookeeper (kafka_2.12-1.1.0/ zookeeper-3.4.13)
- ./kafka-topics.sh –create –topic test_isr –partitions 2 –replication-factor 2 –zookeeper localhost:2181
- broker with id’s : 0, 1, 2
- ./kafka-producer-perf-test.sh –throughput 1000 –record-size 1024 –topic learn_compact –num-records 100000 –producer-props acks=1 bootstrap.servers=192.168.0.167:9092,192.168.0.167:9093,192.168.0.167:9094
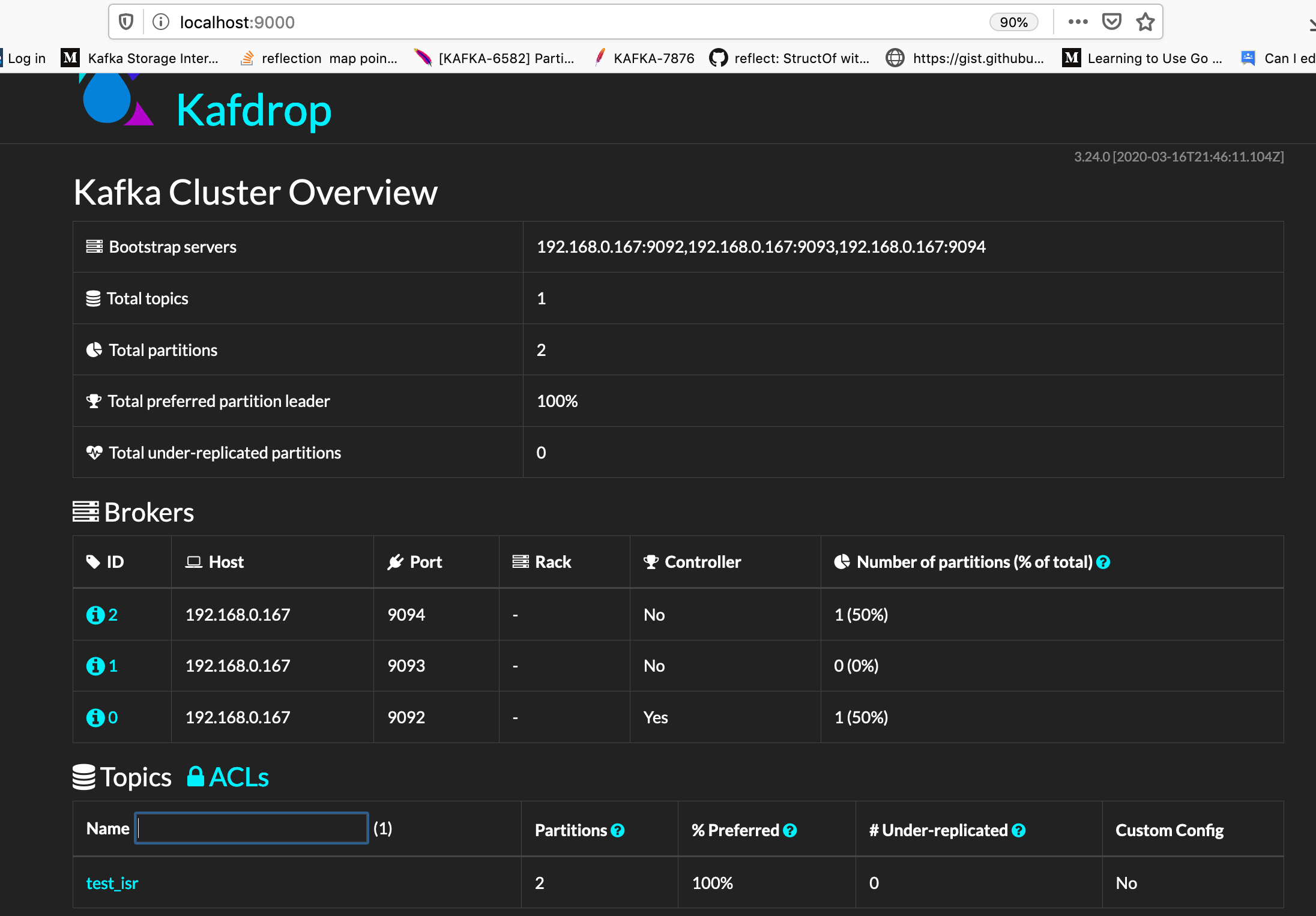
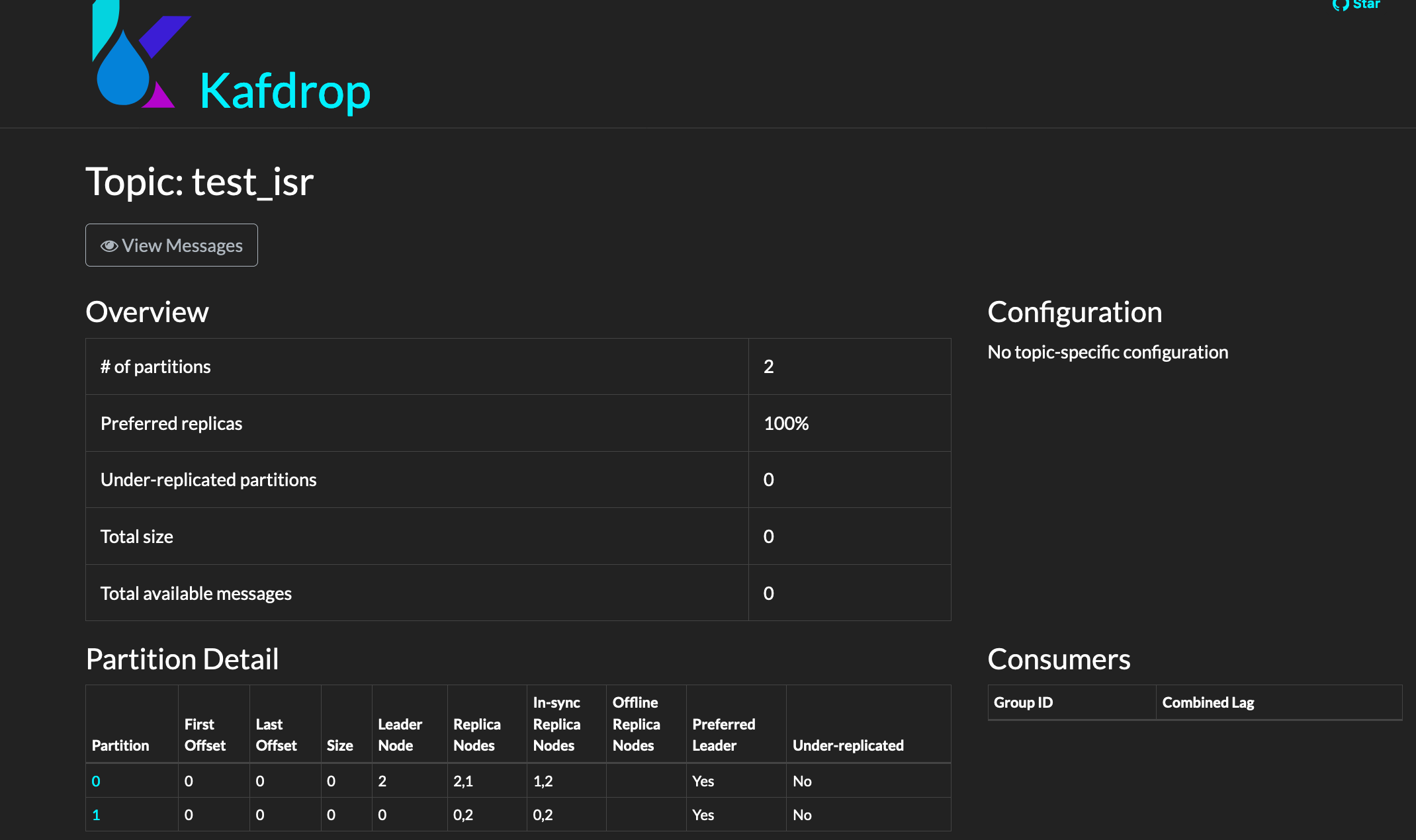
We notice here that brokerId: 1, is not a leader. lets focus on this guy for test simplicity.
Test Starting:
- brokers up
- start the perf producer
- after 2 iterations of producing stop/kill broker id: 1,
- wait for perf producer to finish.
- You shall notice that brokerid: 1 is now out of ISR and partition 0 is under replicated.
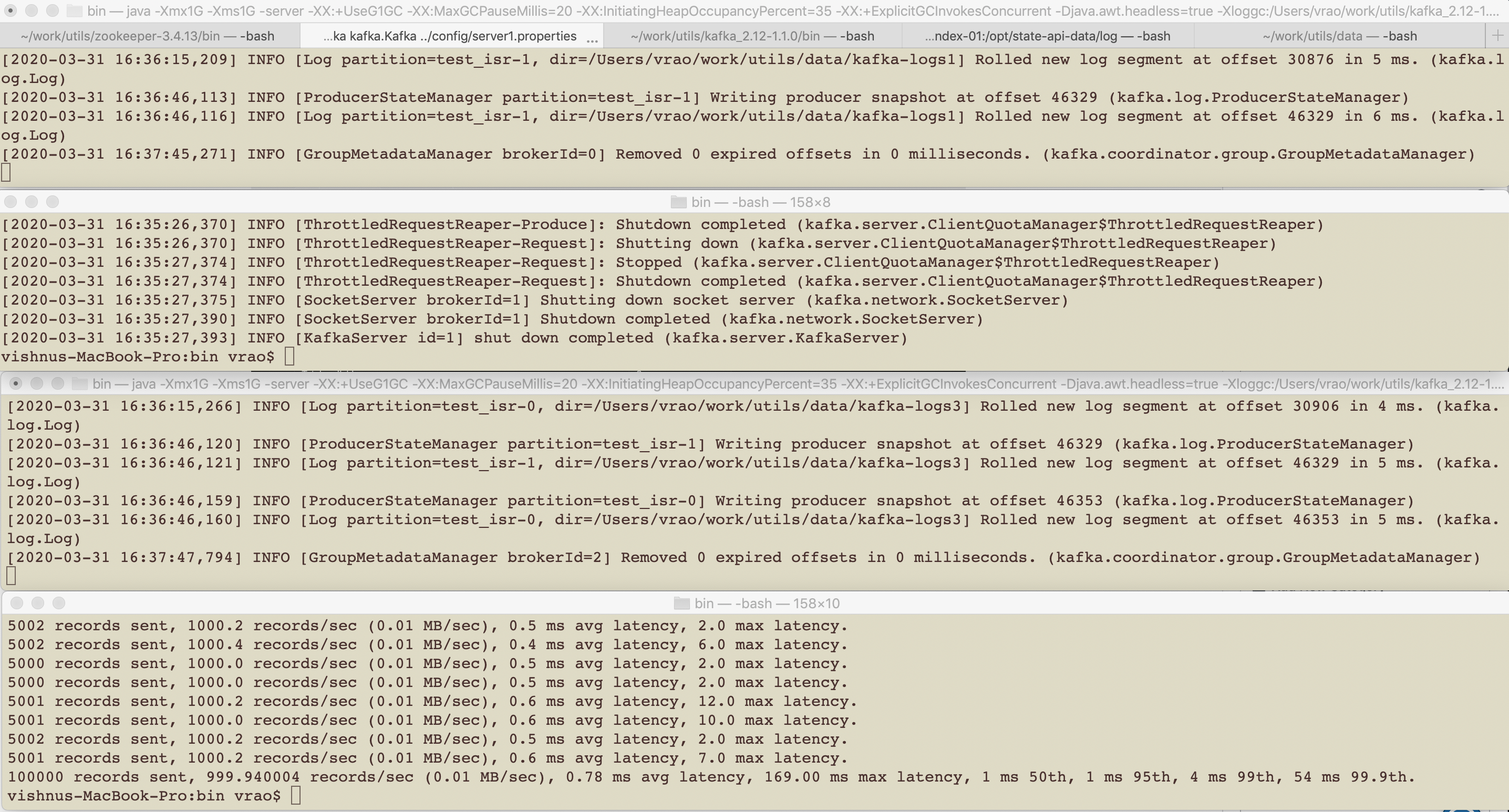
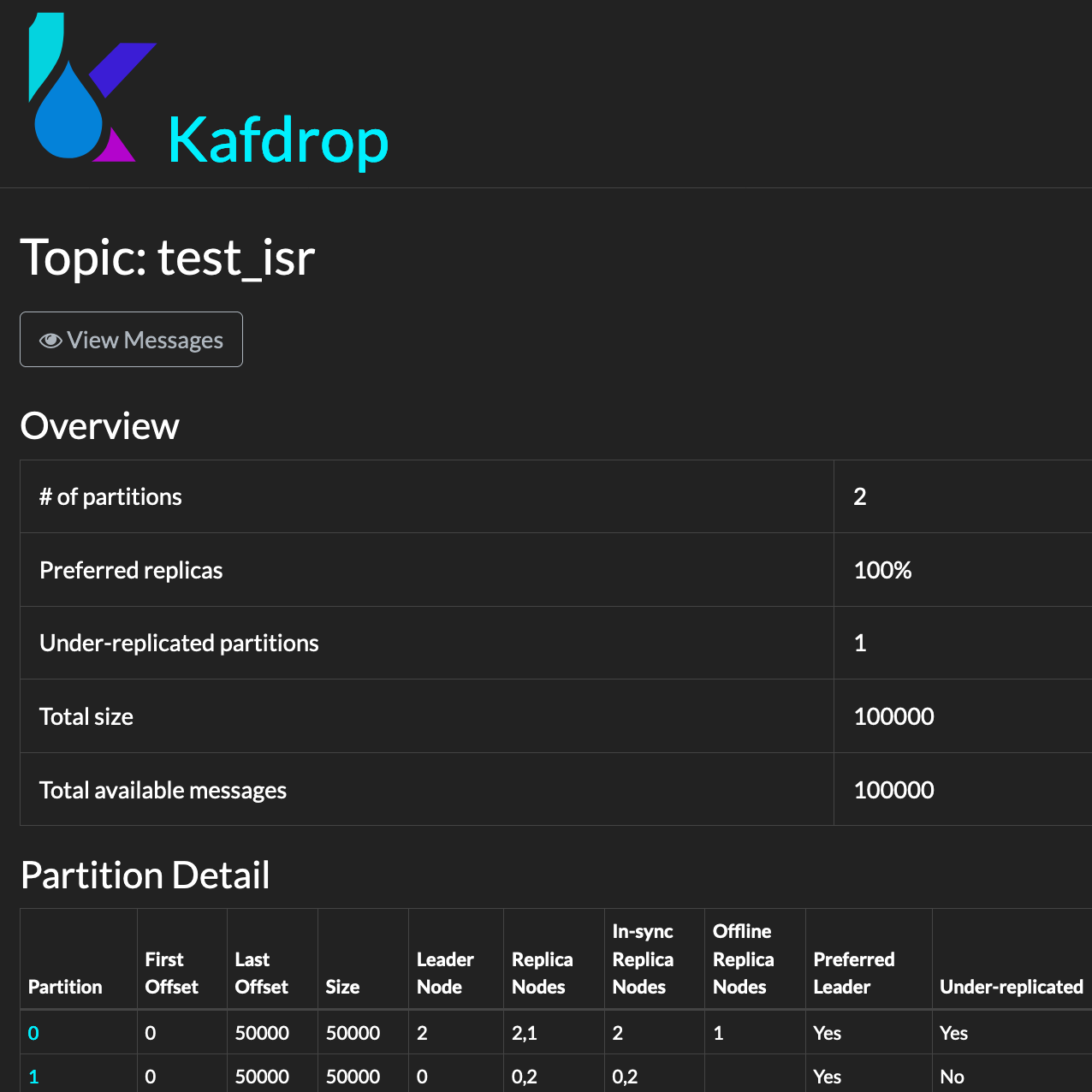
Broker 1 is out of ISR & partition 0 is under replicated and we have 100k messages published.
Recovery for Partition 0:
Note: my kafka log dirs is for brokers 0 , 1, 2 are following respectively
- /Users/vrao/work/utils/data/kafka-logs1. –> broker 0
- /Users/vrao/work/utils/data/kafka-logs2. –> broker 1
- /Users/vrao/work/utils/data/kafka-logs3. –> broker 2
On broker id : 1
1. Go to the partition dir and move existing data to a backup dir.
-
mkdir /tmp/backup_test_isr-0;
-
mv /Users/vrao/work/utils/data/kafka-logs2/test_isr-0/* /tmp/backup_test_isr-0/
2. Stop Leader Broker i.e brokerId 2. (i.e. stop further writes)
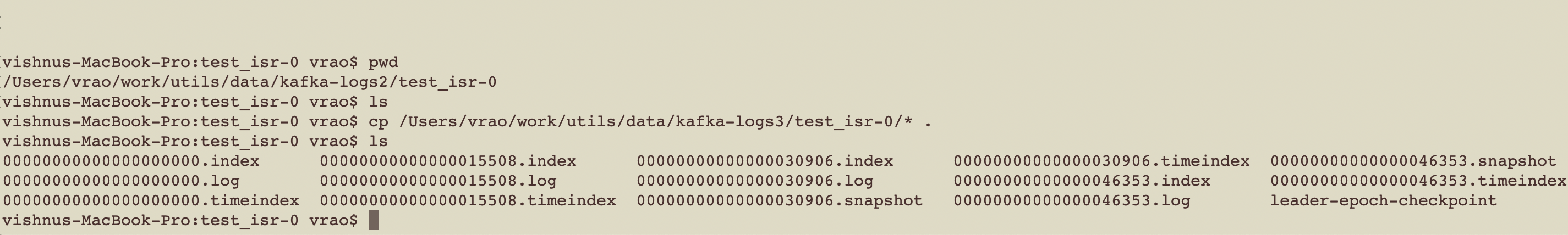
3. Copy data from of partition 0 from broker 2 to broker 1:
4. Now Find the latest replicated offset in brokerId 2 from replication-offset-checkpoint file.
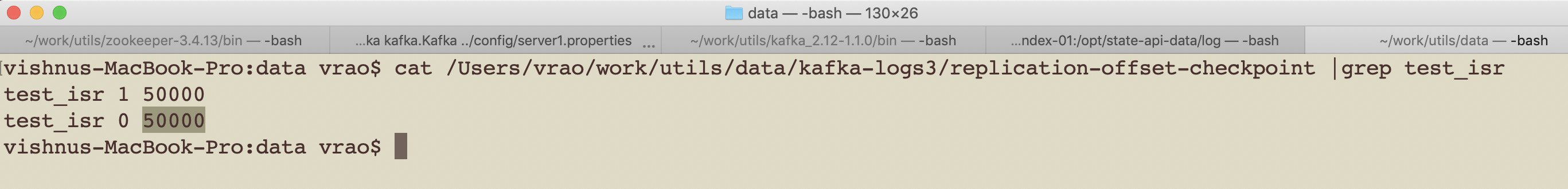
its 50000 for partition 0 of topic test_isr
4.1 Now edit replication-offset-checkpoint of broker 1 and update the value to 50000.
Before editing, you will notice the offset it has replicated is less than 50k i.e.

Now modify file and update 5514 to 50k. (5514 means it was able to replicate successfully upto offset 5514).
After modification file should be as follows:

5. Now Find the latest check pointed offset in brokerId 2 from recovery-point-offset-checkpoint file.

5.1 Now edit recovery-point-offset-checkpoint of broker 1 and update the value to 46353.
Before editing, you will notice something like

Now modify file and update 5515 to 46353. (5515 means it was able to checkpoint successfully upto offset 5515).
After modification file should be as follows:

6. Now follow the same steps (5/5.1 or 4/4.1) with the file log-start-offset-checkpoint
i.e. <log.dir>/log-start-offset-checkpoint
Make sure that the offset for partition 0 for our topic in leader broker is the same in replica broker.
i.e. copy the value of partition 0 from /Users/vrao/work/utils/data/kafka-logs3/log-start-offset-checkpoint to /Users/vrao/work/utils/data/kafka-logs2/log-start-offset-checkpoint.
If the file is empty or has no data , then u have nothing to do 🙂
7. Now we are ready to start broker id: 1
You will notice it joins cluster and ISR has expanded back !
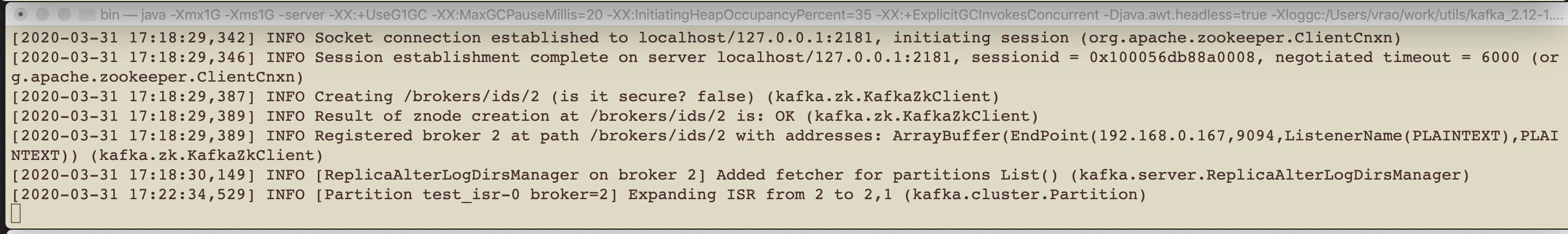
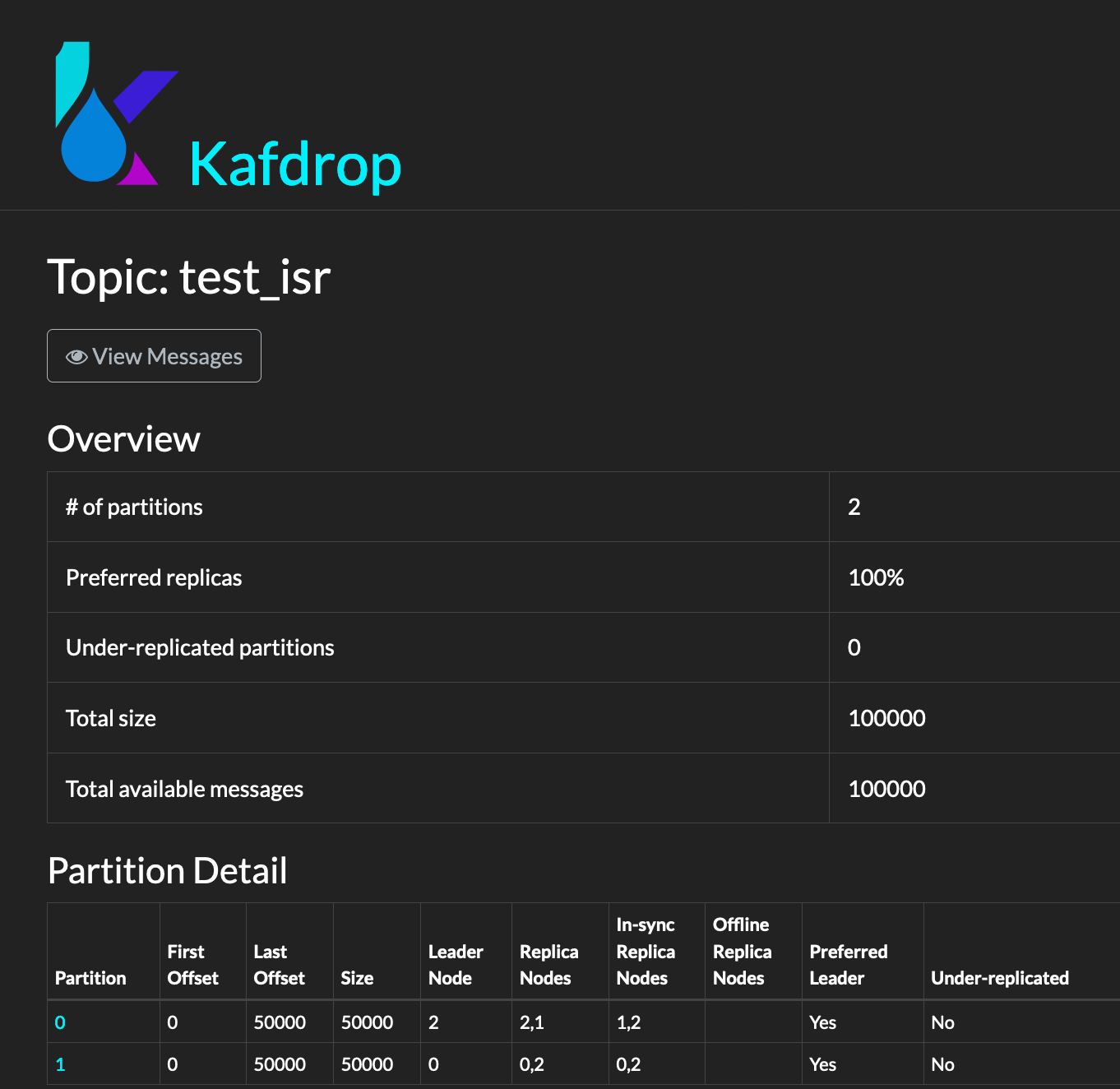
8. Now lets verify if things are good with regard to number of messages.
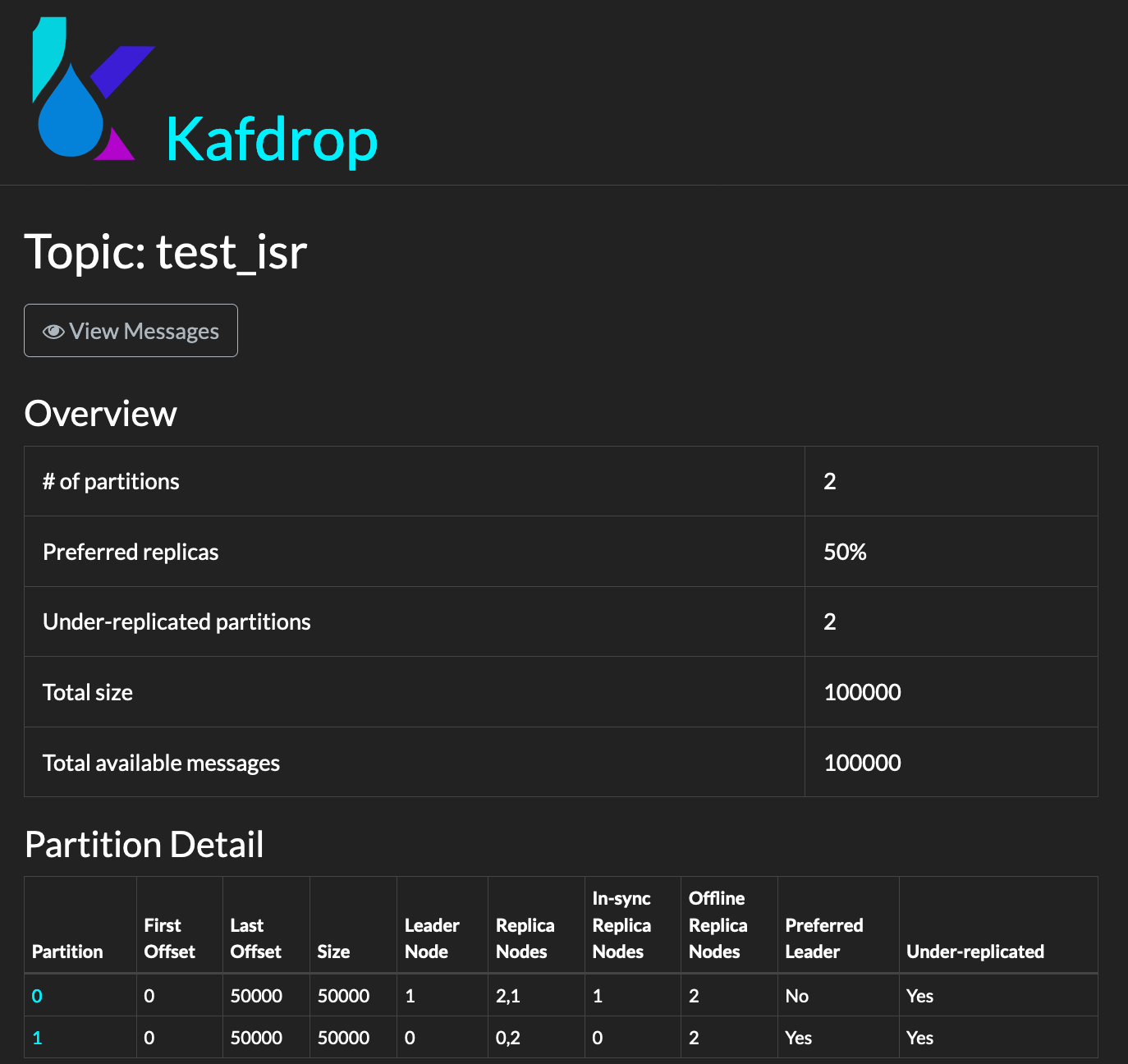
Shut down the leader node i.e. brokerId: 2 so that our replica becomes the new leader.
From our test partition 1 was never affected so it will have 50k msgs and now our replica has become leader for partition 0 i.e. for other 50k msgs.
so we should get 100k msgs.
The following screenshot shows that our replica is now leader (brokerId :1 is leader) and erstwhile leader is offline.
9. Now start a consumer to the topic and you should get 100k msgs.
./kafka-console-consumer.sh –topic test_isr –bootstrap-server 192.168.0.167:9092,192.168.0.167:9094 –from-beginning

So recovery is complete ! We were able to recover data from the erstwhile out of ISR broker and partition is no longer under replicated.
Ps: i did a video recording for same scenario for 50k msgs here, u can find part1 here and part2 here
Ps: I have seen some blog posts where people manually move data and edit the checkpoint files & recover brokers. i hope the above steps are logical . Hope to try in production! Will update if i do. From my test, things look promising.
and as always feedback is welcome.
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
References:
My thanks to the authors of :
View at Medium.com
https://medium.com/@durgaswaroop/a-practical-introduction-to-kafka-storage-internals-d5b544f6925f
http://ixiaosi.art/2019/05/20/kafka/kafka启动分析/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/35407090/explain-replication-offset-checkpoint-and-recovery-point-offset-in-kafka
for some details on log-start-offset-checkpoint u may see refer to this kafka confluence page too. Search for ‘log-begin-offset-checkpoint’
Tools used:
https://github.com/obsidiandynamics/kafdrop


























![Scylla : received an invalid gossip generation for peer [How to resolve] Scylla : received an invalid gossip generation for peer [How to resolve]](https://mash213.files.wordpress.com/2019/07/screenshot-2019-07-05-at-14.44.46.png?w=619)